Electric Car Air Conditioning System
With electric vehicles on the rise, all major countries are implementing a 10-year plan to grow their EV market share by 30%, and with automotive manufacturers working towards EVs as their main inventory across all makes and models, whether you like it or not one day you will be driving an electric vehicle.
Understanding more about electric cars’ air conditioning system and how it works will help you not only be more knowledgeable but can help you identify problems you might have in the future.
But, unlike the A/C in combustion vehicles where its sole purpose is to cool or heat up the cabin, the A/C in electric cars not only helps cool/heat your cabin, but it also helps cool or provides heat to the batteries which provide the energy to the electric motor and all the electrical components within the vehicle.
The truth is, electric vehicles are more reliant on the A/C than combustion motor vehicles.
Table of Contents
How does the AC work in Electric Vehicles?
As electric vehicles are considered the new future, they must have the same features as traditional cars. One of them is, of course, the air conditioning system.
Unlike traditional vehicles, which provide the power for the heating, ventilation, and air-conditioning system, electric vehicles do things completely differently. Electric vehicles don’t have engines, so delivering power to the AC and just about everything else is determined by the amount of stored battery energy.
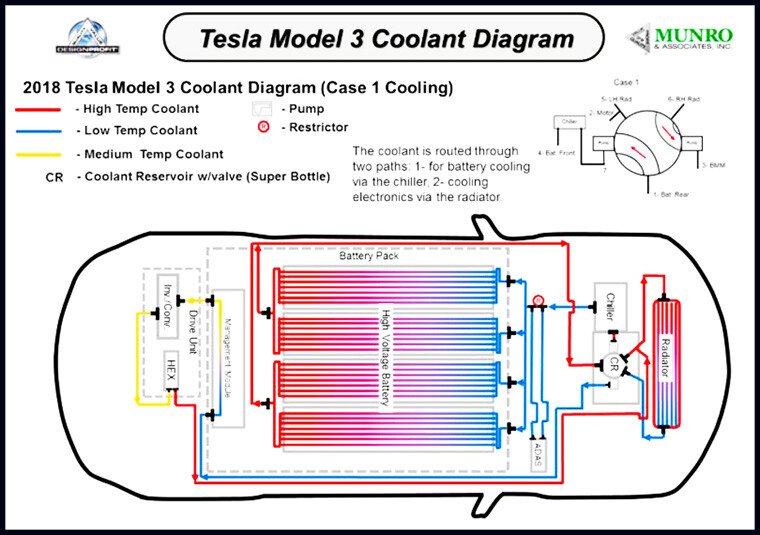
In the case of Tesla EVs, for example, the AC compressor is located at the front of the car and draws power from the Energy Storage System, or ESS, in the back.
What Runs the A/C Compressor?
An air conditioning system cannot work without a compressor, whether it’s installed in a traditional vehicle, an electrical one, or in a building. A compressor is central to the whole unit as it is responsible for circulating or pumping oil and refrigerant through the system.
In vehicles with a conventional internal combustion engine, the a/c compressor is usually driven via a pulley and the V-belt but in electric vehicles, this mechanism is not available.
The a/c compressor in EVs is driven by an electric motor integrated into the vehicle’s high-voltage network and performs two major functions critical for cooling the air.
- First Function
The first is raising the refrigerant’s pressure to make its temperature reach a point that is higher than the temperature of the air present in the surrounding environment. This is important as without that happening, there would not be a heat transfer taking place. - Second Function
The second vital operation that the compressor carries out is that of creating an air pressure within the evaporator that is low. When a low-pressure condition prevails inside the evaporator, the refrigerant boils and vaporizes.
Why do EV Batteries need to Be Cooled?
EV Batteries have specific operating ranges, which are critical for battery life and performance. They are designed to operate at ambient temperature, which is between 20°C and 25°C. Better control over the battery temperature improves their performance and life.
- During operation, they can withstand temperatures between -30°C and 50°C
- During recharges, they can withstand temperatures between 0°C and 50°C
Batteries generate a lot of heat during operation and their temperature must be brought down within operating ranges. At high temperatures of 70°C and 100°C, thermal runaways can occur, causing a chain reaction that destroys the battery pack.
During fast charges, batteries must be cooled down. This is because the high current going into the battery produces excess heat that must be extracted to preserve the high charging rate and not overheat the battery.
They sometimes also need to be heated up when the temperature is too low or to boost performance. For example, cells cannot be charged below 32°F (0°C). Or, companies like Tesla offer battery preheating in some models to reach high performances, going from 0 to 60 mph in less than 2 seconds.
EV Battery Cooling Methods
EV batteries can be cooled using air cooling or liquid cooling. Liquid cooling is the method of choice to meet modern cooling requirements. Let’s go over both methods to understand the difference.
- Air Cooling
Air cooling uses air to cool the battery and exists in passive and active forms. Passive air cooling uses air from the outdoors or from the cabin to cool or heat the battery. It is usually limited to a few hundred watts of heat dissipation. Active air cooling gets its air intake from an air conditioner, which includes an evaporator and a heater to control the air’s temperature. - Liquid Cooling
Liquid cooling is the most popular cooling technology. It uses a liquid coolant such as water, a refrigerant, or ethylene glycol to cool the battery. The liquid goes through tubes, cold plates, or other components that surround the cells and carry heat to another location, such as a radiator or a heat exchanger.
Does The A/C lower an Electric Vehicles Performance?
With today’s combustion-based vehicles, using the air conditioning system will increase fuel consumption by up to 20%. Still, the air conditioner has a much more noticeable impact on electric cars than combustion engines.
Within the city, using your air conditioner can decrease your car’s range by 30%, while on highways and stretches, this impact gets reduced to 20%-25%.
This reduction becomes even direr if the temperatures outside are extreme, i.e., over 95 degrees Fahrenheit.
Let’s take Tesla EVs, for instance. The AC compressor, in this case, is located at the car’s front, which allows the unit to draw power from the energy storage system (ESS).
For those of you who don’t know, the ESS is located in the back. The amount of energy lost when you are trying to heat your car in extreme cold or when trying to cool it up in extreme winters increases because of the distance it has to travel.
Conclusion
When it comes to electric vehicles, the air conditioning system is the most integral component because it does more than just cool or heat up the cabin, it keeps the battery cells and their electrical components running at optimal performance by regulating their temperatures while you drive.
Without a split system, your electric vehicle would cease to run and with more and more motorists driving electric vehicles, an air conditioning issue is something you cannot afford to ignore because if your battery cells and electrical components become damaged, you’re looking at 10’s of thousands in repairs and replacements.
Stay vigilant, and stay educated as we move towards a new era in on-road vehicles and their air conditioning systems.




